Презентація на тему «Education in Great Britain» (варіант 3)

Education in Great Britain

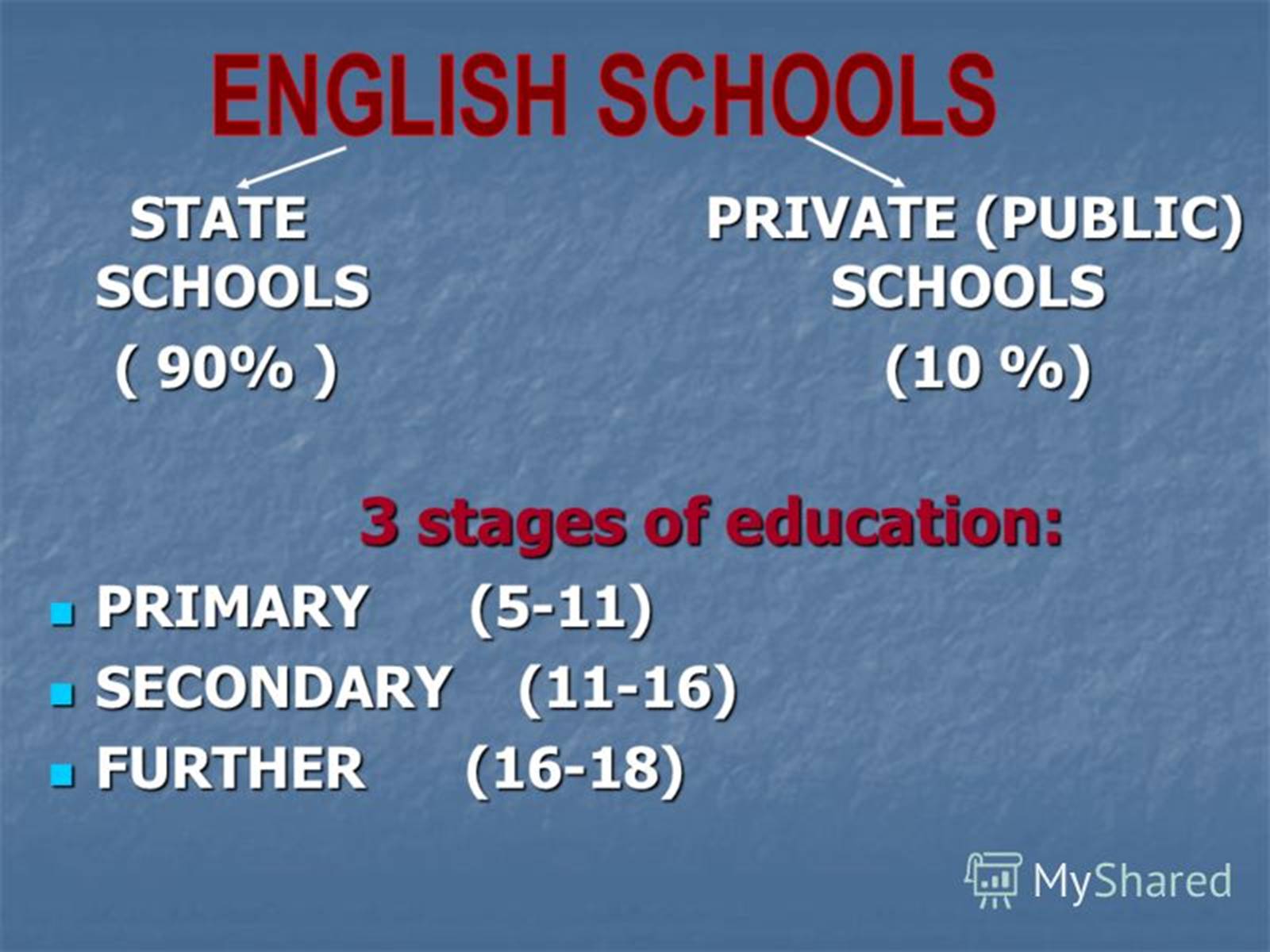
Twelve million children attend about 40.000 schools in Britain. Education in Great Britain is compulsory and free for all children between the ages of 5 and 16. There are many children who attend a nursery school from the age of 3, but it is not compulsory. In nursery schools they learn some elementary things such as numbers, colours, and letters. Apart from that, babies play, have lunch and sleep there. Whatever they do, there is always someone keeping an eye on them.

Compulsory education begins at the age of 5 when children go to primary school. Primary education lasts for 6 years. It is divided into two periods: infant schools (pupils from 5 to 7 years old) and junior schools (pupils from 7 to 11 years old). In infant schools children don't have real classes. They mostly play and learn through playing. It is the time when children just get acquainted with the classroom, the blackboard, desks and the teacher. But when pupils are 7, real studying begins. They don't already play so much as they did it in infant school. Now they have real classes, when they sit at desks, read, write and answer the teacher's questions.
Radyr Primary School, Cardiff, Wales

Compulsory secondary education begins when children are 11 or 12 and lasts for 5 years. Secondary school is traditionally divided into 5 forms: a form to each year. Children study English, Mathematics, Science, History, Art, Geography, Music, a Foreign language and have lessons of Physical training. Religious education is also provided. English, Mathematics and Science are called "core" subjects. At the age of 7,11 and 14 pupils take examinations in the core subjects.

There are 3 types of state secondary schools in Great Britain. They are:
1) comprehensive schools, which take pupils of all abilities without exams. In such schools pupils are often put into certain sets or groups, which are formed according to their abilities for technical or humanitarian subjects. Almost all senior pupils (around 90 per cent) go there;
2) grammar schools, which give secondary education of a very high standard. Entrance is based on the test of ability, usually at 11. Grammar schools are single sexed schools;
3) modern schools, which don't prepare pupils for universities. Education in such schools gives good prospects for practical jobs.

After finishing the fifth form pupils can make their choice: they may either leave school and go to a Further Education College or continue their education in the sixth form. Those who stay at school after GCSE, study for 2 more years for "A' (Advanced) Level Exams in two or three subjects which is necessary to get a place at one of British universities.
St John's College, Cambridge university.
University College London

After leaving secondary school young people can apply to a university, a polytechnic or a college of further education.
There are 126 universities in Britain. They are divided into 5 types:
The Old ones, which were founded before the 19th century, such as Oxford and Cambridge;
The Red Brick, which were founded in the 19th or 20th century;
The Plate Glass, which were founded in 1960s;
The Open University It is the only university offering extramural education. Students learn subjects at home and then post ready exercises off to their tutors for marking;
The New ones. They are former polytechnic academies and colleges.
Cambridge University
British University in Egypt

Universities usually select students basing on their A-level results and an interview.
After three years of study a university graduate get the Degree of a Bachelor of Arts, Science or Engineering. Many students then continue their studies for a Master's Degree and then a Doctor's Degree
Cambridge University
Universities usually select students basing on their A-level results and an interview.
After three years of study a university graduate get the Degree of a Bachelor of Arts, Science or Engineering. Many students then continue their studies for a Master's Degree and then a Doctor's Degree
Cambridge University

EDUCATION IN UKRAINE

The system of secondary education in Ukraine includes primary forms and junior and senior secondary forms.
Children usually go to school at the age of 6 or 7.
There are some preschool institutions, like nursery schools or kindergartens, but they are not obligatory.

Primary forms comprise 1 to 4 forms.
Junior secondary forms comprise 5 to 9 forms.
After the 9th form children can enter tech nical schools of different types.
Those who want to enter higher educational institutions should complete 10—11 forms.
Students can also enter higher education al institutions after graduating from spe cialized colleges or lyceums.
They prepare students in different fields, whether the humanities or the sciences.
Some of them are organized under the authorities of higher educational establishments.
The system of higher education is presented by universities, polytechnic institutes or specialized
institutes.

Universities offer a fiveyear course of study and usually have from six to twelve.
Institutes train specialists for industry, agriculture and economy. Students are also offered post graduate education and scientific research work.
Nowadays due to the state of our national economy not many young people are en gaged in the research work
Recently a great number of private educational establishments have appeared.
Some institutions have feepaying groups or departments.
The students may get education there at the same high level as in the state in stitutions.

The work was done Tulchevska Maria